Razer, one of the leading global companies providing gaming hardware, has announced the acquisition of 100% of the shares of Go Touch VR SAS, also known as Interhaptics, a French startup founded in 2017 specialising in haptics tools and software. Razer showcased its haptics ecosystem – HyperSense – in 2018 for the first time, supported by the company’s gaming peripherals. The developments over the past few years, however, have only led to the use of HyperSense in a few headset models. Now, with the acquisition of Interhaptics, Razer will be looking to expand HyperSense across more products to build out a full ecosystem of peripherals with haptic features.
Razer is not the only gaming company that has invested much in haptic technology. Coming with the PS5 console, Sony’s DualSense controller is a revolutionary product in terms of utilising haptics in gaming. Not only does it adopt the high-fidelity LRA-enabled vibration, but the DualSense is also the first controller to include kinaesthetic haptic feedback in the back triggers for enhanced effects. The DualSense implements some patented technologies from General Vibration, a US haptics technology company.
Haptics have become ubiquitous in daily life, found in different devices, particularly smartphones. However, simple rumbling no longer meets the customers’ expectations. The real trend and motivation behind the market is to create a more immersive user experience with haptic feedback. This is not only valid in the gaming industry but also in extended reality (VR, AR & MR). The ultimate goal is to simulate the real sense of touch when the user interacts with the product. The haptic effect is not limited to vibration, but can potentially be extended to sensing surface texture, forces, temperature, and more.
The predominant technologies for haptics as of 2022 are eccentric rotating mass (ERM) motors and linear resonant actuators (LRAs). These haptic motors are widely used in gaming products and are used in most gaming controllers (eg Xbox controllers), while LRAs are seen in more recent products such as the Nintendo Switch and the Steam Deck. But more advanced technologies are being demanded, including voice coil motors (VCMs), piezoelectric actuators, etc. The new technologies with higher value-adds drive the growth of the haptics market in the long-term future.
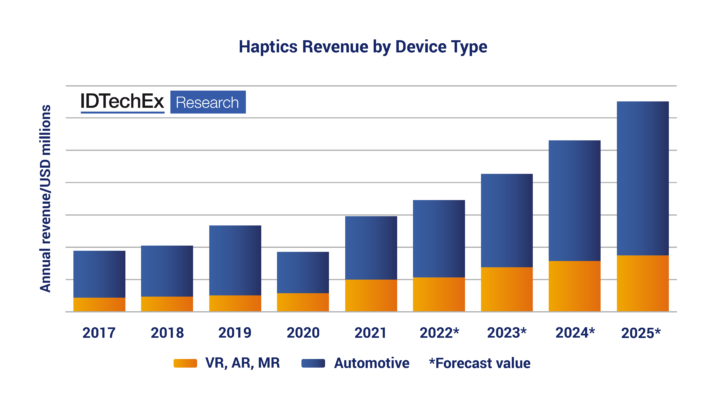
In addition to new technologies, new markets can also be an important factor driving market growth. Examples of markets with promising opportunities for haptic implementations include automotive and XR. Haptics in extended reality create an immersive experience for users. In vehicles, however, haptics currently tend to be used for safety alerts. For example, some cars have haptic steering wheels that will vibrate to alert the driver when the car is deviating from the lane. In the future picture, haptics will mean more than safety alerts in vehicles. Haptics can be a significant interface for interacting with the autonomous driving system. When fully autonomous driving becomes a reality, the car may become a centre of relaxation and entertainment, and the use of haptics in vehicles may be focused on enhancing user experience, like in other devices.







